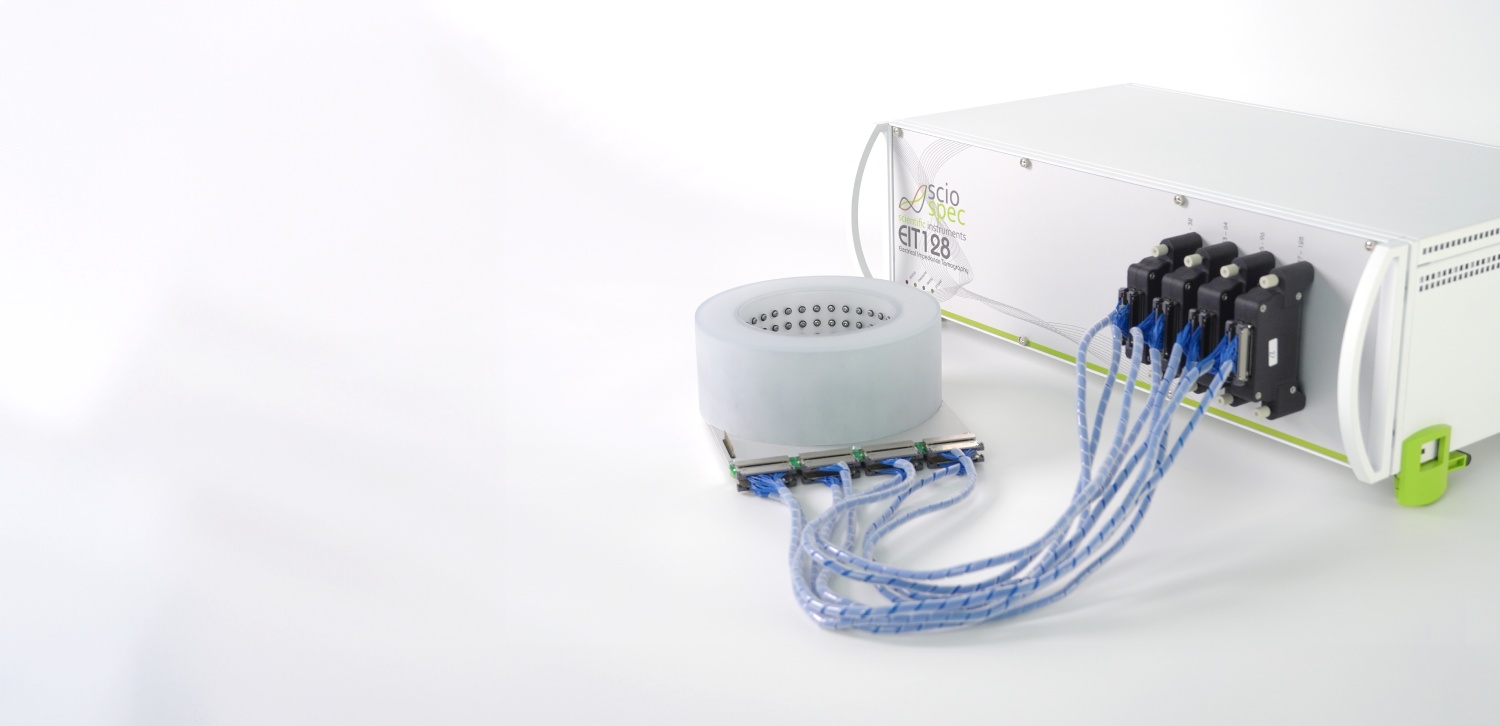
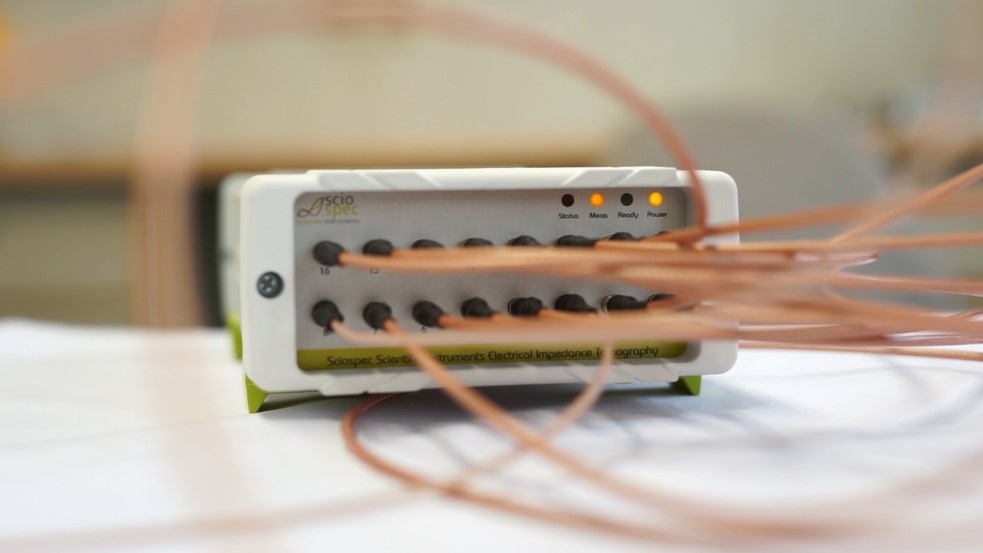
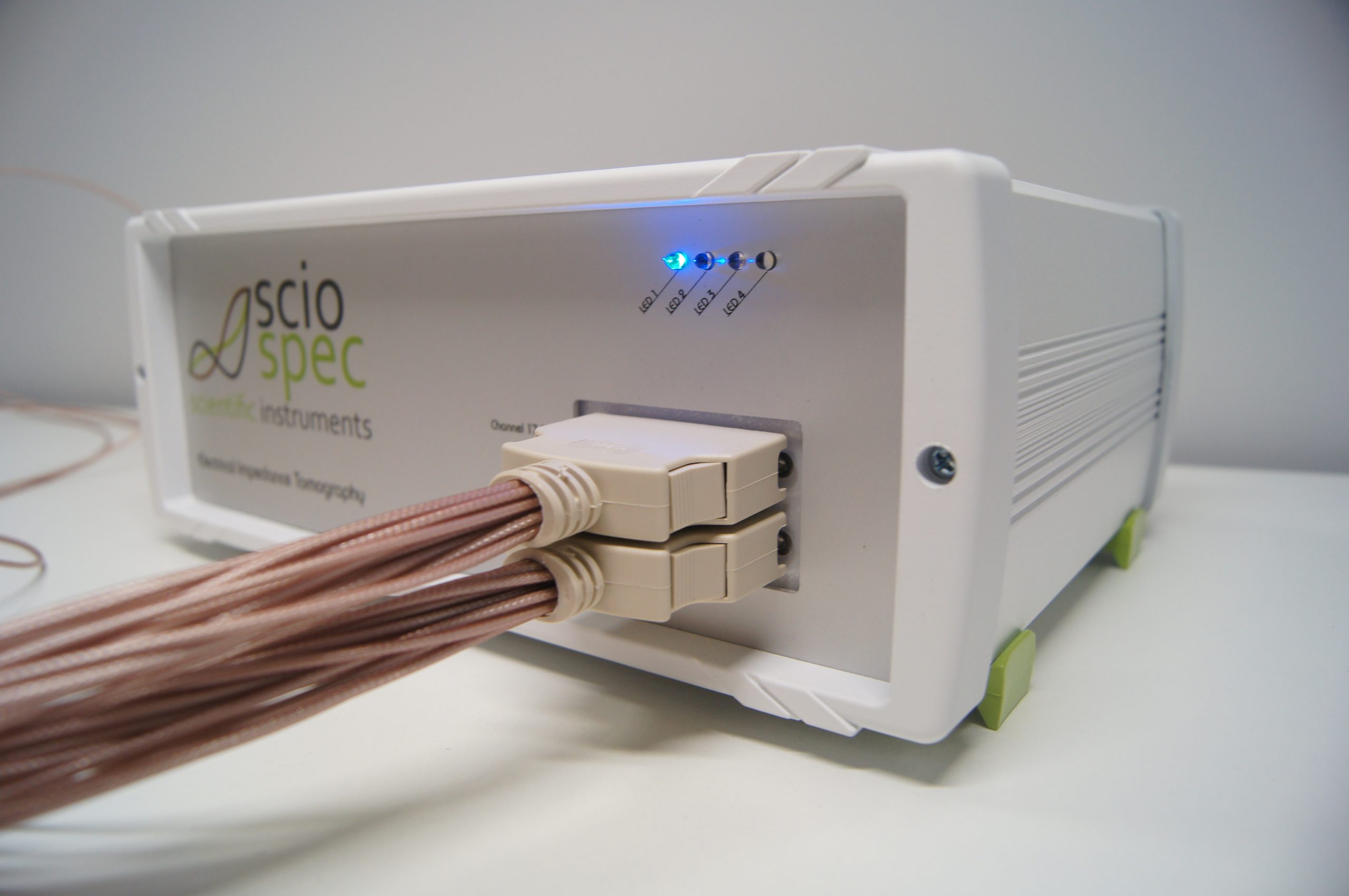
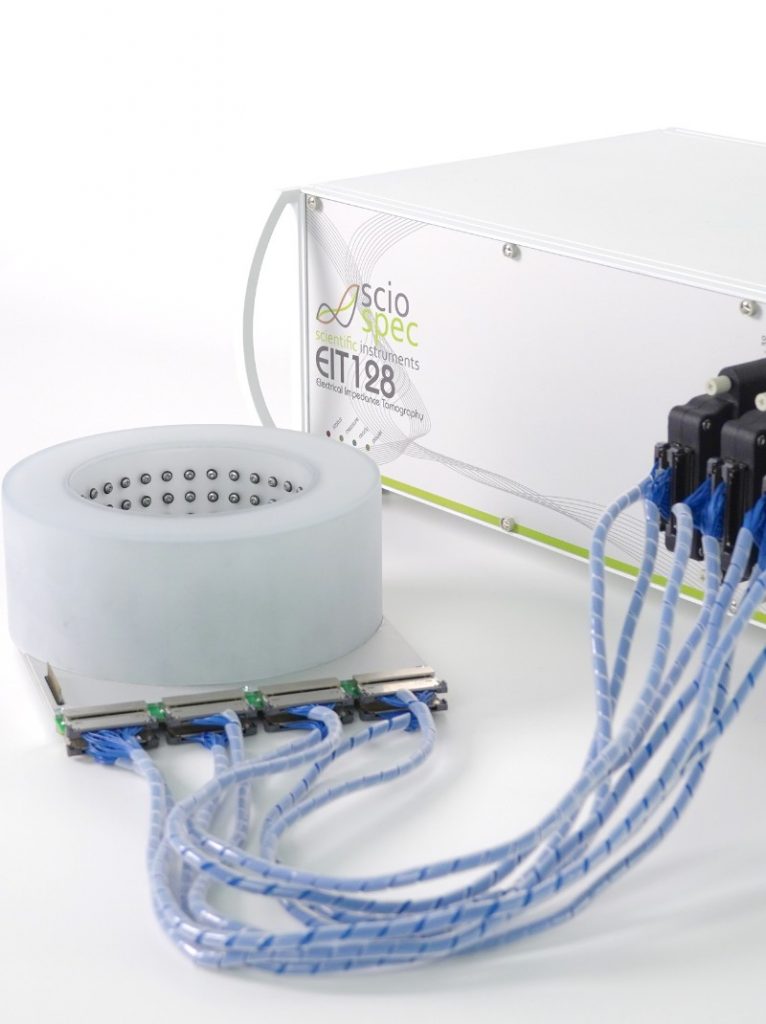
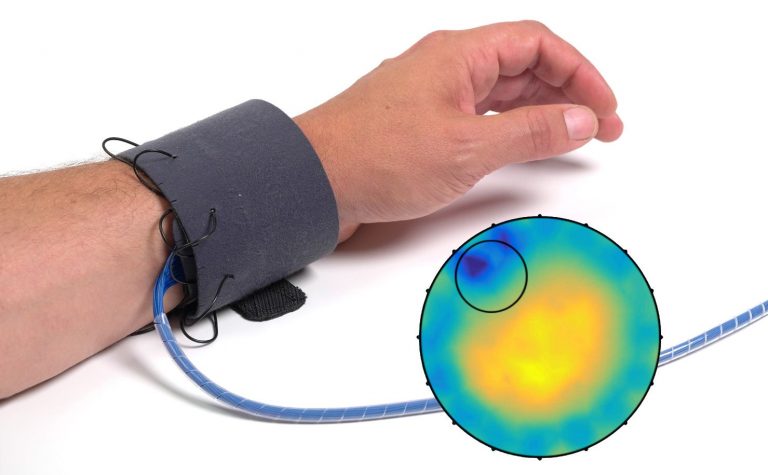
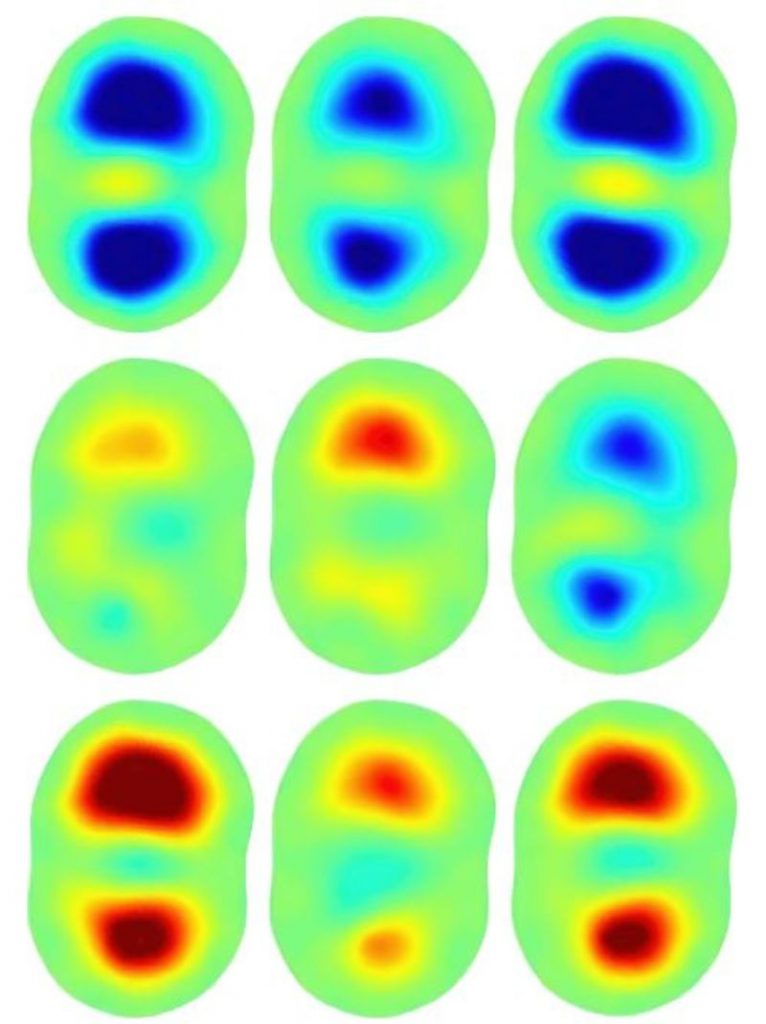
Wassergehaltsbestimmung von tablettierten Pharmazeutika
Der Wassergehalt von Pharmazeutika ist ein entscheidender Faktor für viele Aspekte in der pharmazeutischen Industrie. Er beeinflusst unter anderem Funktion, Stabilität, Qualität, Haltbarkeit und Lagerfähigkeit